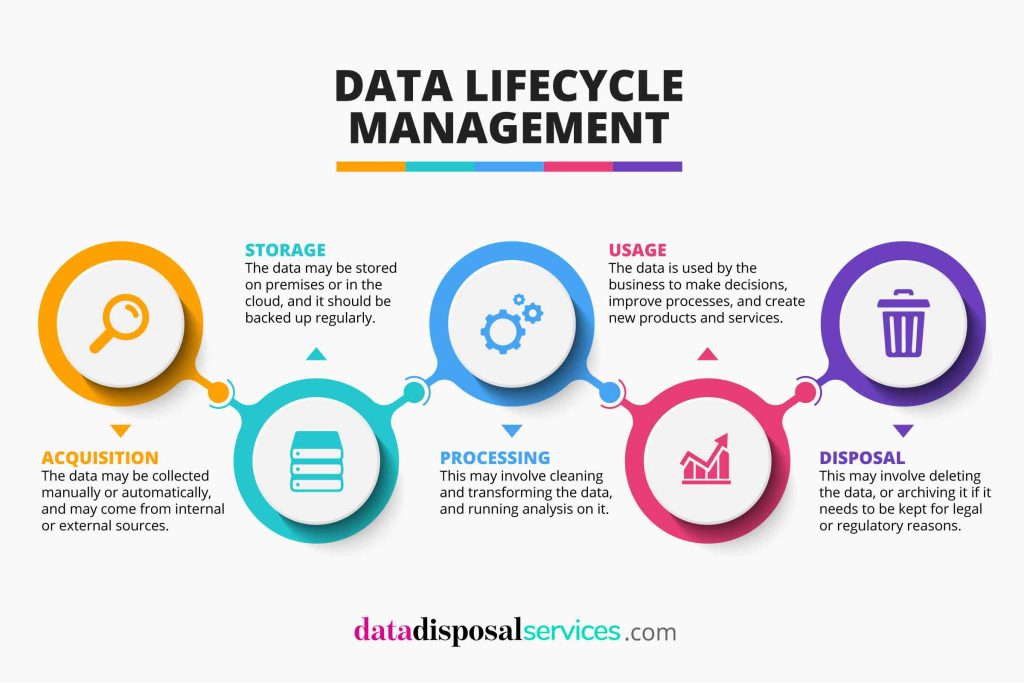
Which of the following most accurately describes data lifecycle management (DLM)? Data lifecycle management (DLM) is a systematic approach to handling the flow of data from creation to deletion. It encompasses several crucial phases, each tailored to optimize data utility and ensure security throughout its lifecycle.
Understanding the Phases of Data Lifecycle Management
Data lifecycle management structures the handling of data into distinct stages. This segmentation aids in addressing specific needs at each phase, ensuring efficient management and utilization of information.
Data Entry and Capture
The lifecycle begins with Data Capture, ensuring accuracy right from the inception point. This phase focuses on gathering data correctly to minimize errors and inconsistencies that could affect later stages.
Secure Storage Solutions
Following capture, Data Storage is critical. It involves securing data in controlled environments to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches, crucial for maintaining confidentiality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Consistent Data Processing
In the Data Processing stage, data undergoes transformation and validation to ensure it meets quality standards. This phase guarantees that the data is consistent, reliable, and suitable for business insights and decision-making.
Data Retention Strategies
Data Retention policies dictate the duration for which data is kept active for access and use. Effective retention strategies ensure data is available as needed without consuming unnecessary resources.
Responsible Data Disposal
The final phase, Data Disposal, involves the secure and responsible elimination of data that is no longer required. This stage protects sensitive information from potential security threats.
| Phase | Focus | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Capture | Accuracy at source | Reduces errors |
| Storage | Security | Prevents breaches |
| Processing | Consistency | Ensures quality |
| Retention | Accessibility | Optimizes resources |
| Disposal | Security | Protects sensitive info |
Ensuring Integrity and Trust in Data Management
Data lifecycle management not only supports data integrity by maintaining the trustworthiness and accuracy of data throughout its lifecycle but also plays a pivotal role in regulatory compliance and strategic business planning. By adhering to defined lifecycle stages, businesses ensure that data remains accurate, complete, and consistent, vital for informed decision-making and maintaining consumer trust.
Final Insights on Data Lifecycle Mastery
Through effective data lifecycle management, businesses enhance their operational efficiency and data governance. Which of the following most accurately describes data lifecycle management (DLM)? It is an essential strategy that ensures data remains robust, secure, and actionable from inception to obsolescence, supporting key business processes and compliance requirements.


